Quick facts
- Carpenter ants are very common in Minnesota.
- They can potentially damage homes and other wooden structures.
- The best method for controlling carpenter ants is to deliver insecticide into their nest.
- Because controlling carpenter ants is complex, it's best to hire a pest management professional (pest control technician) to eliminate nests.
Identifying carpenter ants
Carpenter ants are among the largest ants in Minnesota. There are several species that may be found infesting homes and other buildings.
How to recognize carpenter ants:
- They have a waist with one node (petiole) and a thorax (area behind the head) that is evenly rounded when viewed from the side.
- Workers are black or red and black.
- Workers usually range in size from 3/8 to 1/2 inch long; one species is only 3/16 inch.
- Even carpenter ant workers of the same species vary in size (major and minor workers).
- Queens and males are larger than workers and have wings. Queens lose their wings once they start a new nest.
- Queens may be as large as one inch long.
Other ants can be mistaken for carpenter ants. They have one or two nodes and an uneven thorax when viewed in profile. They usually do not infest wood.
Correct identification of the ants is important for control strategies to work effectively.
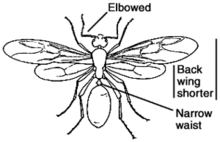
Ant or termite?
Carpenter ants have dark-colored bodies, narrow waists, elbowed (bent) antennae and hind wings that are shorter than front wings (if wings are present).
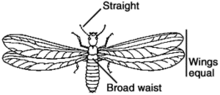
Termites are very uncommon in Minnesota.
- Workers are light-colored, have broad waists and straight antennae.
- They avoid light and are rarely seen outside of their colony.
- Winged termites, queens and kings, are dark-colored and have wings of equal length.
Biology
- Carpenter ants feed on sources of protein and sugar.
- Outdoors, they feed on living and dead insects.
- They feed on a sweet liquid produced by aphids and scale insects, called honeydew.
- Indoors, carpenter ants feed on meats and pet food, as well as syrup, honey, sugar, jelly and other sweets.
- Carpenter ants do not eat wood. They remove wood as they create galleries and tunnels for nesting.
They search for food between sunset and midnight, during spring and summer months. Sometimes workers travel up to 100 yards from a nest in search of food.
Carpenter ants get into houses when they travel back and forth between their main nest and their satellite nests.
There are two types of carpenter ant nests: parent nests and satellite nests.
- Parent nest are usually found outdoors in decaying wood in trees, tree roots, tree stumps and logs or boards lying on or buried in the ground.
- Areas around windows and where wood parts touch the foundation may also be prone to infestation.
In homes, parent nest are found in moist or decayed wood (caused by exposure to water leaks, condensation, or poor air circulation). Typical sites include:
- Behind bathroom tiles.
- Around tubs, sinks, showers and dishwashers.
- Under roofing, in attic beams and under subfloor insulation.
- In hollow spaces such as doors, curtain rods and wall voids.
- They can also nest in foam insulation.
Parent carpenter ant colonies sometimes establish one or more satellite nests in nearby indoor or outdoor sites. The workers of satellite colonies move frequently between their nest and the parent colony. Satellite nests are typically composed of workers, pupae and mature larvae.
For this reason, satellite nests can be found in relatively dry locations, such as insulation, hollow doors, sound wood and wall voids (the eggs would dry out in lower humidity).
It is common to find carpenter ants in homes during spring. It is important to determine whether the ants are coming from the outside or inside your home. Their presence is not enough to say that there is a nest in your home.
Finding carpenter ants in your home during late winter or early spring means the ants are coming from a nest in the building. If you see activity later in the year, it may be less clear if the nest is in the building
Finding large numbers of winged ants indoors is a sure sign that a nest exists inside your home. However, finding one or just a few winged queens does not mean a nest is present indoors. The queens probably had just mated and entered the home searching for nesting sites. When they land after mating, their wings break off.
Wingless queens found indoors are not an indication of an indoor nest. They are new queens that have recently shed their wings and are still searching for nesting sites.
Seeing carpenter ants indoors during winter means that there is an inside nest. Sometimes worker ants are carried in with firewood, but these workers are not able to start nests or cause any damage in homes.
When the nest receives enough warmth from sunlight, mild outdoor temperatures or from indoor heat, workers become active at night, searching for moisture, and can be seen around cabinets, sinks, dishwashers, rolled-up towels, bathroom tubs, sink and toilet areas. On a bright sunny day, ants may be seen walking through different areas of the house.
A carpenter ant nest can exist in a house during winter but not be noticed. If the nest is in a place that does not receive sufficient indoor heat or sunshine, such as a north-facing outside wall, the ants will remain dormant until spring.
Damage
Carpenter ants damage wood by excavating and creating galleries and tunnels for their nest. These areas are clean, do not contain sawdust or other debris, and are smooth with a well-sanded appearance.
The damage to wood structures is variable. The longer a colony is present in a structure, the greater the damage that can be done. Structural wood can be weakened when carpenter ant damage is severe. Generally, damage occurs slowly, often taking years to occur.
Prevention and control
To prevent carpenter ant problems indoors, eliminate high moisture conditions.
- Replace moisture-damaged wood.
- Prevent moisture from wood or lumber that is stored in a garage or near the house by elevating it to allow air circulation.
- Store firewood as far away from buildings as possible.
- Remove tree and shrub stumps and roots.
- Trim branches that overhang the home, so branches don't touch the house (including roof and eaves).
- Prune branches that touch electrical lines. Carpenter ants can travel from branches to lines and use them to get into buildings.
In order to eliminate carpenter ants nesting indoors, you need to locate and destroy their nest. This is often challenging as nests are hidden and not easily discovered. Careful observations of worker ants will help you find the nest. Observe worker ants between sunset and midnight during spring and summer months.
- Use a flashlight with a red film over the lens. Ants cannot see red light and won’t be disturbed by it.
- Or cover part of the flashlight with your hand so it is less bright to follow carpenter ants.
You can increase your chances of following workers to their nest by setting out food that they like. Many foods are attractive to carpenter ants.
- During spring, carpenter ants are particularly attracted to protein sources, such as tuna packed in water. (They don't like tuna packed in oil.)
- Set out small pieces of tuna for the ants to take back to their nest. It is easier to follow the ants when they are carrying food.
- Place food close to where carpenter ants are active so they can easily find it.
Carpenter ants are attracted to honey and other sweet foods.
Other signs that indicate a carpenter ant nest is present:
- Finding coarse sawdust.
- Consistent indoor sightings of large numbers of worker ants (20 or more).
- Large numbers of winged ants indoors (late winter through spring).
Examine areas where steady moisture is or has been a problem. These are a few common locations:
- Firewood stored in an attached garage, next to the foundation, along an outside wall, or in a basement.
- Areas around the plumbing or vent entrances.
- Trees with branches overhanging and touching the house or contacting utility wires.
Pest management professionals may use a moisture meter to find areas prone to carpenter ants.
Listen for sounds that may indicate a nest:
- An active colony may make a dry, rustling sound that becomes louder if the colony is disturbed.
- Tap the suspected area and press an ear to the surface to hear any sound.
Pest management professionals may use a stethoscope to locate a nest.
If one nest is found, there may be more nests in a structure.
The best way to control carpenter ants is to locate and destroy the nest, replace damaged or decayed wood, and eliminate any moisture problems.
Eliminating a carpenter ant nest can be difficult because of the hidden nature of the nest. Carpenter ant control is usually best done by an experienced pest management professional. They have the experience, equipment and a wider array of products to more effectively control a carpenter ant problem.
You can help by telling the pest management professional about when, where and how many ants you've seen.
There can be more than one nest in a building, but only treat nests that have been discovered.
Indoor treatment with dust or liquid pesticides
Spraying foraging workers is not effective. It may temporarily reduce the number of ants you see. However, this will not eliminate a nest because:
- Ants carry very little insecticide back to their nests.
- Most ants forage outside and do not come in contact with the insecticides.
- Only a relatively small percentage of a colony's population is out foraging at any given time.
Nests are often hidden in wall voids, ceilings, subfloors, attics or hollow doors. It is sometimes necessary for a professional pest management applicator to drill small (about 1/8 inch) holes and apply insecticidal dust into the nest area. Don't do this yourself.
Determine the nest's location as specifically as possible. Control should not be applied randomly through the home.
If the nest is exposed (for instance due to remodeling or reroofing), you can use a liquid or aerosol ready-to-use insecticide.
- Common products include cyfluthrin, cypermethrin, deltamethrin or permethrin.
- The more of the colony that is exposed, the better your chance of destroying it.
- Be prepared to find a carpenter ant colony and have a product ready at the start of construction.
- Once the nest is exposed, that portion of the colony will try to relocate to protect themselves.
Indoor treatment with baits
- If you can't find the nest, you may be able to control it with bait (a food source combined with a slow-acting poison).
- Ants need to eat the bait and return to the nest.
- Baits are effective because ants share their food with others in the nest. If enough bait is moved into a nest, it will be destroyed.
- Carpenter ants have complex food preferences and baits may not attract ants long enough to be successful.
Baits available for ant control are liquid or gel and commonly contain:
- Avermectin
- Borax
- Fipronil
- Spinosad
The keys to successful baiting are placement and monitoring.
- Place the bait only in areas where activity has been seen or is strongly suspected.
- Monitor the bait over 24 hours for feeding activity.
- Bait that is ignored should be cleaned up and substituted with another.
- If bait is consumed, add more.
- Be patient—baits can take weeks or months to achieve control.
- Never apply insecticides on or around baits because this will prevent feeding.
CAUTION: Mention of a pesticide or use of a pesticide label is for educational purposes only. Always follow the pesticide label directions attached to the pesticide container you are using. Be sure that the area you wish to treat is listed on the label of the pesticide you intend to use. Remember, the label is the law.
Often, carpenter ant nests found indoors are satellite nests that can be traced back to a parent colony outdoors.
Look for nests in:
- Trees
- Stumps
- Roots
- Fence posts
- Landscape timbers
- Other wood structures
Try removing the wood with the parent colony. When that is not possible, contact a professional to treat the carpenter ant nest.
Trim branches that overhang buildings or electrical wiring to avoid giving carpenter ants easy access to your home.
Control in trees
Carpenter ants nest in trees in one of two situations:
- In rotted, decayed wood.
- In the center heartwood section of a tree.
Parts of a tree can rot or become weak because of insects, disease or drought. Carpenter ants use knots, cracks, holes and old insect tunnels to find entry into these areas.
- The ants do not harm the tree and only take advantage of preexisting soft, weak wood to establish their colony.
- Control is not necessary for the tree's health.
Control of carpenter ants in trees is important if ants are entering homes from colonies in trees. Contact a pest management professional if control is necessary.
CAUTION: Mention of a pesticide or use of a pesticide label is for educational purposes only. Always follow the pesticide label directions attached to the pesticide container you are using. Be sure that the area you wish to treat is listed on the label of the pesticide you intend to use. Remember, the label is the law.
In most cases, you need a pest management professional to treat carpenter ants. Pest management professionals are experienced in inspecting properties, locating nests, baiting techniques and correct application of pesticides. So, they can more effectively and quickly control carpenter ants.
They also have access to specialized equipment and insecticides, such as Termidor and Talstar, and they know how to correctly use them.
Pest management professionals may also offer services such as sealing or screening holes and crevices to help prevent further carpenter ant activity in homes.
Reviewed in 2020